原文:
Layered Noise
Layered Noise
目前为止,我们创建的噪声要么非常光滑,要么过于随机。我们可以将它们结合起来,从而实现一种多层次的噪声图。这样我们可以得到既平滑又细节丰富的噪声图。我们前面介绍过的值类噪声和泊林噪声都可以应用到本章的叠加噪声中。虽然叠加噪声产生的效果可能更符合你的预期,但是因为叠加了多个噪声图,所以其性能消耗也是叠加的。
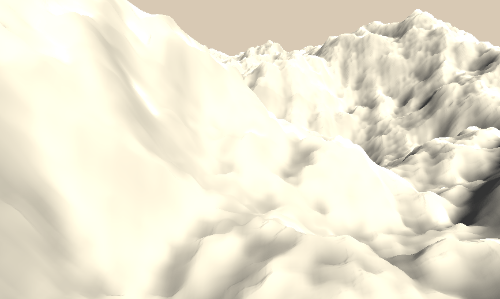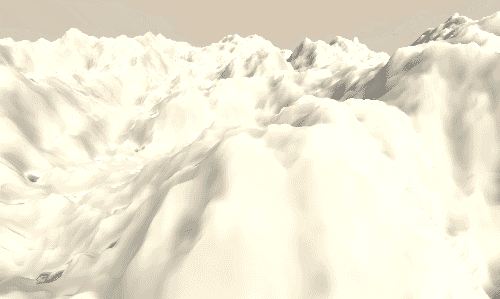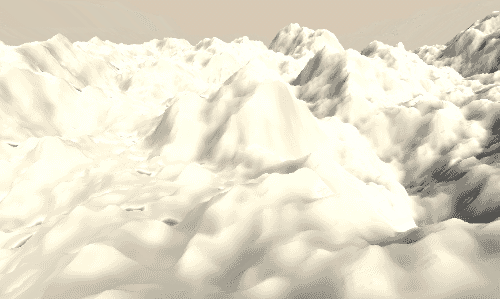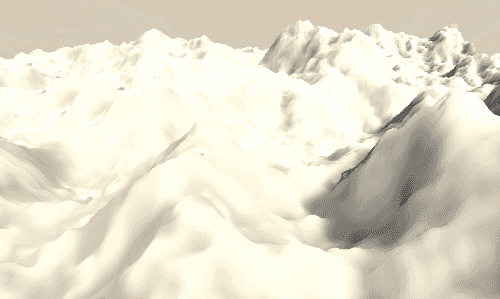
Layered 1d Noise
在前面的教程中,我们实现的噪声图可以通过控制色块的大小,进而控制噪声的频率。

和之前一样,我们首先从一维开始做起。不过我们需要采集两次噪声,一次是和原来一样,一次是乘以2。乘以2的操作实际上就是提高它的频率。然后我们将高频噪声的值降低,高频低强度的噪声可以用来表示细节,然后将其叠加到低频噪声上。
为了便于大家理解,这里我还是照常贴出相关源码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| float sampleLayeredNoise(float value){
float noise = gradientNoise(value);
float highFreqNoise = gradientNoise(value * 6);
noise = noise + highFreqNoise * 0.2;
return noise;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| void surf (Input i, inout SurfaceOutputStandard o) {
float value = i.worldPos.x / _CellSize;
float noise = sampleLayeredNoise(value);
float dist = abs(noise - i.worldPos.y);
float pixelHeight = fwidth(i.worldPos.y);
float lineIntensity = smoothstep(2*pixelHeight, pixelHeight, dist);
o.Albedo = lerp(1, 0, lineIntensity);
}
|

上面简单的叠加已经能达到一些效果了,一次叠加获得比较粗糙的细节。不过我们还可以继续叠加。我们将叠加的层数称为阶,所以我们现在是二阶叠加噪声。
为了实现高阶叠加噪声,我们将使用循环语句。同时我们的阶数也可以使用宏命令来设置为常量,这样可以在材质面板上调节。当然我们也可以将阶数完全用变量来表示,但是使用变量控制的循环语句,是没办法进行展开优化的,所以应该尽量避免。这里每个层的频率变量乘以上一个层的实际频率,得到当前层的实际频率。我们叫这个频率变量为粗糙度,或者说相对于上一层的粗糙度。我们每一层之间的相对粗糙度取同一个值,所以所有层的相对粗糙度都为_persistance。然后还有一个从整体上控制粗糙度的量_Routhness。
1
2
3
4
5
| Properties {
_CellSize ("Cell Size", Range(0, 2)) = 2
_Roughness ("Roughness", Range(1, 8)) = 3
_Persistance ("Persistance", Range(0, 1)) = 0.4
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
#define OCTAVES 4
float _CellSize;
float _Roughness;
float _Persistance;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| float sampleLayeredNoise(float value){
float noise = 0;
float frequency = 1;
float factor = 1;
[unroll]
for(int i=0; i<OCTAVES; i++){
noise = noise + gradientNoise(value * frequency + i * 0.72354) * factor;
factor *= _Persistance;
frequency *= _Roughness;
}
return noise;
}
|

Layered multidimensional Noise
多维噪声图的实现方式类似,只不过相应的噪声函数输入参数要改为对应维度的向量。这里我们以二维为例。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| float sampleLayeredNoise(float2 value){
float noise = 0;
float frequency = 1;
float factor = 1;
[unroll]
for(int i=0; i<OCTAVES; i++){
noise = noise + perlinNoise(value * frequency + i * 0.72354) * factor;
factor *= _Persistance;
frequency *= _Roughness;
}
return noise;
}
|
下面是三维。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| float sampleLayeredNoise(float3 value){
float noise = 0;
float frequency = 1;
float factor = 1;
[unroll]
for(int i=0; i<OCTAVES; i++){
noise = noise + perlinNoise(value * frequency + i * 0.72354) * factor;
factor *= _Persistance;
frequency *= _Roughness;
}
return noise;
}
|
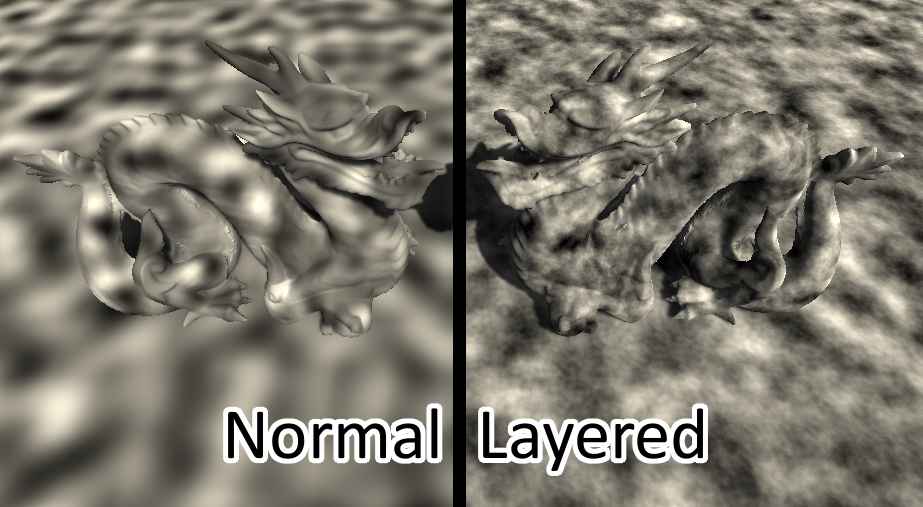
Special Use Case
另一个经常用到噪声的场景是高度图。通常我们处理纹理是在片段着色器中,但是当处理高度图时,我们是在顶点着色器中采样的,然后将采样结果叠加到顶点的y坐标。关于这部分的内容,你可以参考之前关于顶点偏移的介绍。
首先,我们修改表面着色器的宏命令部分。添加顶点处理函数,#pragma surface surf Standard fullforwardshadows vertex:vert addshadow。然后实现顶点处理函数,其中将采样噪声叠加到顶点的y坐标,然后计算顶点世界坐标。然后在表面着色器中,将光照参数albedo设置为白色。如果我们想让其表现的更细致,应该使用分辨率更高的网格数据,否者的话看到的将是很明显的多边形网格。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| Properties {
_CellSize ("Cell Size", Range(0, 10)) = 2
_Roughness ("Roughness", Range(1, 8)) = 3
_Persistance ("Persistance", Range(0, 1)) = 0.4
_Amplitude("Amplitude", Range(0, 10)) = 1
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| void vert(inout appdata_full data){
float4 worldPos = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, data.vertex);
float3 value = worldPos / _CellSize;
float noise = sampleLayeredNoise(value) + 0.5;
data.vertex.y += noise * _Amplitude;
}
|
1
2
3
| void surf (Input i, inout SurfaceOutputStandard o) {
o.Albedo = 1;
}
|
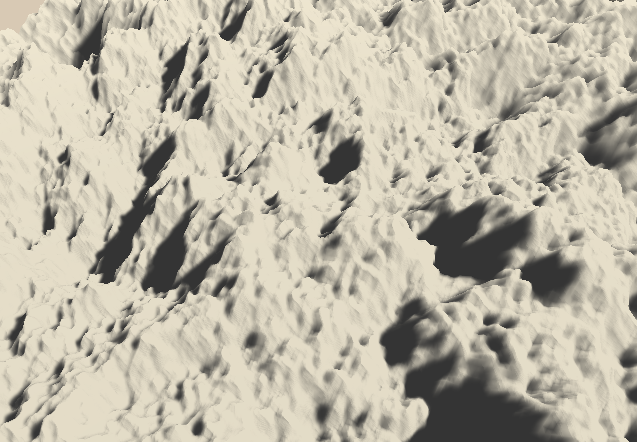

到目前为止,虽然我们修改了顶点位置,但是在阴影处理的时候还是被当做平面来看。我们可以让其根据新的顶点位置重新计算阴影,这一点在顶点偏移中有介绍。
在这里我遇到一个问题,就是传入的顶点齐次坐标的w值并不为1,也就是说该坐标是缩放后的坐标。因此我们需要执行齐次除法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| void vert(inout appdata_full data){
float3 localPos = data.vertex / data.vertex.w;
float3 modifiedPos = localPos;
float2 basePosValue = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, modifiedPos).xz / _CellSize;
float basePosNoise = sampleLayeredNoise(basePosValue) + 0.5;
modifiedPos.y += basePosNoise * _Amplitude;
float3 posPlusTangent = localPos + data.tangent * 0.02;
float2 tangentPosValue = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, posPlusTangent).xz / _CellSize;
float tangentPosNoise = sampleLayeredNoise(tangentPosValue) + 0.5;
posPlusTangent.y += tangentPosNoise * _Amplitude;
float3 bitangent = cross(data.normal, data.tangent);
float3 posPlusBitangent = localPos + bitangent * 0.02;
float2 bitangentPosValue = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, posPlusBitangent).xz / _CellSize;
float bitangentPosNoise = sampleLayeredNoise(bitangentPosValue) + 0.5;
posPlusBitangent.y += bitangentPosNoise * _Amplitude;
float3 modifiedTangent = posPlusTangent - modifiedPos;
float3 modifiedBitangent = posPlusBitangent - modifiedPos;
float3 modifiedNormal = cross(modifiedTangent, modifiedBitangent);
data.normal = normalize(modifiedNormal);
data.vertex = float4(modifiedPos.xyz, 1);
}
|
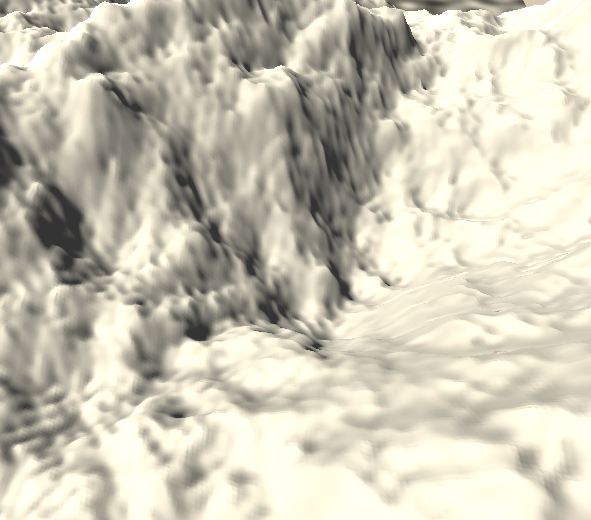
当然,我们也可以引入时间变量,从而达到滚动动画效果。
1
2
|
_ScrollDirection("Scroll Direction", Vector) = (0, 1)
|
1
2
|
float2 _ScrollDirection;
|
1
2
|
float2 basePosValue = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, modifiedPos).xz / _CellSize + _ScrollDirection * _Time.y;
|
1
2
|
float2 tangentPosValue = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, posPlusTangent).xz / _CellSize + _ScrollDirection * _Time.y;
|
1
2
|
float2 bitangentPosValue = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, posPlusBitangent).xz / _CellSize + _ScrollDirection * _Time.y;
|

Source
1d layered noise
https://github.com/ronja-tutorials/ShaderTutorials/blob/master/Assets/027_Layered_Noise/layered_perlin_noise_1d.shader
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
| Shader "Tutorial/027_layered_noise/1d" {
Properties {
_CellSize ("Cell Size", Range(0, 2)) = 2
_Roughness ("Roughness", Range(1, 8)) = 3
_Persistance ("Persistance", Range(0, 1)) = 0.4
}
SubShader {
Tags{ "RenderType"="Opaque" "Queue"="Geometry"}
CGPROGRAM
#pragma surface surf Standard fullforwardshadows
#pragma target 3.0
#include "Random.cginc"
#define OCTAVES 4
float _CellSize;
float _Roughness;
float _Persistance;
struct Input {
float3 worldPos;
};
float easeIn(float interpolator){
return interpolator * interpolator * interpolator * interpolator * interpolator;
}
float easeOut(float interpolator){
return 1 - easeIn(1 - interpolator);
}
float easeInOut(float interpolator){
float easeInValue = easeIn(interpolator);
float easeOutValue = easeOut(interpolator);
return lerp(easeInValue, easeOutValue, interpolator);
}
float gradientNoise(float value){
float fraction = frac(value);
float interpolator = easeInOut(fraction);
float previousCellInclination = rand1dTo1d(floor(value)) * 2 - 1;
float previousCellLinePoint = previousCellInclination * fraction;
float nextCellInclination = rand1dTo1d(ceil(value)) * 2 - 1;
float nextCellLinePoint = nextCellInclination * (fraction - 1);
return lerp(previousCellLinePoint, nextCellLinePoint, interpolator);
}
float sampleLayeredNoise(float value){
float noise = 0;
float frequency = 1;
float factor = 1;
[unroll]
for(int i=0; i<OCTAVES; i++){
noise = noise + gradientNoise(value * frequency + i * 0.72354) * factor;
factor *= _Persistance;
frequency *= _Roughness;
}
return noise;
}
void surf (Input i, inout SurfaceOutputStandard o) {
float value = i.worldPos.x / _CellSize;
float noise = sampleLayeredNoise(value);
float dist = abs(noise - i.worldPos.y);
float pixelHeight = fwidth(i.worldPos.y);
float lineIntensity = smoothstep(2*pixelHeight, pixelHeight, dist);
o.Albedo = lerp(1, 0, lineIntensity);
}
ENDCG
}
FallBack "Standard"
}
|
2d layered noise
https://github.com/ronja-tutorials/ShaderTutorials/blob/master/Assets/027_Layered_Noise/layered_perlin_noise_2d.shader
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
| Shader "Tutorial/027_layered_noise/2d" {
Properties {
_CellSize ("Cell Size", Range(0, 2)) = 2
_Roughness ("Roughness", Range(1, 8)) = 3
_Persistance ("Persistance", Range(0, 1)) = 0.4
}
SubShader {
Tags{ "RenderType"="Opaque" "Queue"="Geometry"}
CGPROGRAM
#pragma surface surf Standard fullforwardshadows
#pragma target 3.0
#include "Random.cginc"
#define OCTAVES 4
float _CellSize;
float _Roughness;
float _Persistance;
struct Input {
float3 worldPos;
};
float easeIn(float interpolator){
return interpolator * interpolator;
}
float easeOut(float interpolator){
return 1 - easeIn(1 - interpolator);
}
float easeInOut(float interpolator){
float easeInValue = easeIn(interpolator);
float easeOutValue = easeOut(interpolator);
return lerp(easeInValue, easeOutValue, interpolator);
}
float perlinNoise(float2 value){
float2 lowerLeftDirection = rand2dTo2d(float2(floor(value.x), floor(value.y))) * 2 - 1;
float2 lowerRightDirection = rand2dTo2d(float2(ceil(value.x), floor(value.y))) * 2 - 1;
float2 upperLeftDirection = rand2dTo2d(float2(floor(value.x), ceil(value.y))) * 2 - 1;
float2 upperRightDirection = rand2dTo2d(float2(ceil(value.x), ceil(value.y))) * 2 - 1;
float2 fraction = frac(value);
float lowerLeftFunctionValue = dot(lowerLeftDirection, fraction - float2(0, 0));
float lowerRightFunctionValue = dot(lowerRightDirection, fraction - float2(1, 0));
float upperLeftFunctionValue = dot(upperLeftDirection, fraction - float2(0, 1));
float upperRightFunctionValue = dot(upperRightDirection, fraction - float2(1, 1));
float interpolatorX = easeInOut(fraction.x);
float interpolatorY = easeInOut(fraction.y);
float lowerCells = lerp(lowerLeftFunctionValue, lowerRightFunctionValue, interpolatorX);
float upperCells = lerp(upperLeftFunctionValue, upperRightFunctionValue, interpolatorX);
float noise = lerp(lowerCells, upperCells, interpolatorY);
return noise;
}
float sampleLayeredNoise(float2 value){
float noise = 0;
float frequency = 1;
float factor = 1;
[unroll]
for(int i=0; i<OCTAVES; i++){
noise = noise + perlinNoise(value * frequency + i * 0.72354) * factor;
factor *= _Persistance;
frequency *= _Roughness;
}
return noise;
}
void surf (Input i, inout SurfaceOutputStandard o) {
float2 value = i.worldPos.xz / _CellSize;
float noise = sampleLayeredNoise(value) + 0.5;
o.Albedo = noise;
}
ENDCG
}
FallBack "Standard"
}
|
3d layered noise
https://github.com/ronja-tutorials/ShaderTutorials/blob/master/Assets/027_Layered_Noise/layered_perlin_noise_3d.shader
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
| Shader "Tutorial/027_layered_noise/3d" {
Properties {
_CellSize ("Cell Size", Range(0, 2)) = 2
_Roughness ("Roughness", Range(1, 8)) = 3
_Persistance ("Persistance", Range(0, 1)) = 0.4
}
SubShader {
Tags{ "RenderType"="Opaque" "Queue"="Geometry"}
CGPROGRAM
#pragma surface surf Standard fullforwardshadows
#pragma target 3.0
#include "Random.cginc"
#define OCTAVES 4
float _CellSize;
float _Roughness;
float _Persistance;
struct Input {
float3 worldPos;
};
float easeIn(float interpolator){
return interpolator * interpolator;
}
float easeOut(float interpolator){
return 1 - easeIn(1 - interpolator);
}
float easeInOut(float interpolator){
float easeInValue = easeIn(interpolator);
float easeOutValue = easeOut(interpolator);
return lerp(easeInValue, easeOutValue, interpolator);
}
float perlinNoise(float3 value){
float3 fraction = frac(value);
float interpolatorX = easeInOut(fraction.x);
float interpolatorY = easeInOut(fraction.y);
float interpolatorZ = easeInOut(fraction.z);
float cellNoiseZ[2];
[unroll]
for(int z=0;z<=1;z++){
float cellNoiseY[2];
[unroll]
for(int y=0;y<=1;y++){
float cellNoiseX[2];
[unroll]
for(int x=0;x<=1;x++){
float3 cell = floor(value) + float3(x, y, z);
float3 cellDirection = rand3dTo3d(cell) * 2 - 1;
float3 compareVector = fraction - float3(x, y, z);
cellNoiseX[x] = dot(cellDirection, compareVector);
}
cellNoiseY[y] = lerp(cellNoiseX[0], cellNoiseX[1], interpolatorX);
}
cellNoiseZ[z] = lerp(cellNoiseY[0], cellNoiseY[1], interpolatorY);
}
float noise = lerp(cellNoiseZ[0], cellNoiseZ[1], interpolatorZ);
return noise;
}
float sampleLayeredNoise(float3 value){
float noise = 0;
float frequency = 1;
float factor = 1;
[unroll]
for(int i=0; i<OCTAVES; i++){
noise = noise + perlinNoise(value * frequency + i * 0.72354) * factor;
factor *= _Persistance;
frequency *= _Roughness;
}
return noise;
}
void surf (Input i, inout SurfaceOutputStandard o) {
float3 value = i.worldPos / _CellSize;
float noise = sampleLayeredNoise(value) + 0.5;
o.Albedo = noise;
}
ENDCG
}
FallBack "Standard"
}
|
https://github.com/ronja-tutorials/ShaderTutorials/blob/master/Assets/027_Layered_Noise/layered_noise_special.shader
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
| Shader "Tutorial/027_layered_noise/special_use_case" {
Properties {
_CellSize ("Cell Size", Range(0, 16)) = 2
_Roughness ("Roughness", Range(1, 8)) = 3
_Persistance ("Persistance", Range(0, 1)) = 0.4
_Amplitude("Amplitude", Range(0, 10)) = 1
_ScrollDirection("Scroll Direction", Vector) = (0, 1, 0, 0)
}
SubShader {
Tags{ "RenderType"="Opaque" "Queue"="Geometry"}
CGPROGRAM
#pragma surface surf Standard fullforwardshadows vertex:vert addshadow
#pragma target 3.0
#include "Random.cginc"
#define OCTAVES 4
float _CellSize;
float _Roughness;
float _Persistance;
float _Amplitude;
float2 _ScrollDirection;
struct Input {
float3 worldPos;
};
float easeIn(float interpolator){
return interpolator * interpolator;
}
float easeOut(float interpolator){
return 1 - easeIn(1 - interpolator);
}
float easeInOut(float interpolator){
float easeInValue = easeIn(interpolator);
float easeOutValue = easeOut(interpolator);
return lerp(easeInValue, easeOutValue, interpolator);
}
float perlinNoise(float2 value){
float2 lowerLeftDirection = rand2dTo2d(float2(floor(value.x), floor(value.y))) * 2 - 1;
float2 lowerRightDirection = rand2dTo2d(float2(ceil(value.x), floor(value.y))) * 2 - 1;
float2 upperLeftDirection = rand2dTo2d(float2(floor(value.x), ceil(value.y))) * 2 - 1;
float2 upperRightDirection = rand2dTo2d(float2(ceil(value.x), ceil(value.y))) * 2 - 1;
float2 fraction = frac(value);
float lowerLeftFunctionValue = dot(lowerLeftDirection, fraction - float2(0, 0));
float lowerRightFunctionValue = dot(lowerRightDirection, fraction - float2(1, 0));
float upperLeftFunctionValue = dot(upperLeftDirection, fraction - float2(0, 1));
float upperRightFunctionValue = dot(upperRightDirection, fraction - float2(1, 1));
float interpolatorX = easeInOut(fraction.x);
float interpolatorY = easeInOut(fraction.y);
float lowerCells = lerp(lowerLeftFunctionValue, lowerRightFunctionValue, interpolatorX);
float upperCells = lerp(upperLeftFunctionValue, upperRightFunctionValue, interpolatorX);
float noise = lerp(lowerCells, upperCells, interpolatorY);
return noise;
}
float sampleLayeredNoise(float2 value){
float noise = 0;
float frequency = 1;
float factor = 1;
[unroll]
for(int i=0; i<OCTAVES; i++){
noise = noise + perlinNoise(value * frequency + i * 0.72354) * factor;
factor *= _Persistance;
frequency *= _Roughness;
}
return noise;
}
void vert(inout appdata_full data){
float3 localPos = data.vertex / data.vertex.w;
float3 modifiedPos = localPos;
float2 basePosValue = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, modifiedPos).xz / _CellSize;
float basePosNoise = sampleLayeredNoise(basePosValue) + 0.5;
modifiedPos.y += basePosNoise * _Amplitude;
float3 posPlusTangent = localPos + data.tangent * 0.02;
float2 tangentPosValue = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, posPlusTangent).xz / _CellSize;
float tangentPosNoise = sampleLayeredNoise(tangentPosValue) + 0.5;
posPlusTangent.y += tangentPosNoise * _Amplitude;
float3 bitangent = cross(data.normal, data.tangent);
float3 posPlusBitangent = localPos + bitangent * 0.02;
float2 bitangentPosValue = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, posPlusBitangent).xz / _CellSize;
float bitangentPosNoise = sampleLayeredNoise(bitangentPosValue) + 0.5;
posPlusBitangent.y += bitangentPosNoise * _Amplitude;
float3 modifiedTangent = posPlusTangent - modifiedPos;
float3 modifiedBitangent = posPlusBitangent - modifiedPos;
float3 modifiedNormal = cross(modifiedTangent, modifiedBitangent);
data.normal = normalize(modifiedNormal);
data.vertex = float4(modifiedPos.xyz, 1);
}
void surf (Input i, inout SurfaceOutputStandard o) {
o.Albedo = 1;
}
ENDCG
}
FallBack "Standard"
}
|
高阶叠加噪声可以很好的模拟复杂的噪声图案。你也可以试着将不同类型的噪声进行叠加,然后看看会产生什么现象。总之,我希望你们能够理解其中的基本原理,然后肉会贯通。如果你发现有任何理解不了的地方,可以给我留言。
希望你能喜欢这个教程哦!如果你想支持我,可以关注我的推特,或者通过ko-fi、或patreon给两小钱。总之,各位大爷,走过路过不要错过,有钱的捧个钱场,没钱的捧个人场:-)!!!







